Introduction:
Refrigerators are an indispensable part of modern households, providing us with a convenient way to store and preserve our food. Behind their sleek exteriors, refrigerators are equipped with an array of intricate components that work together to ensure optimal cooling performance. In this article, we will delve into the various parts that make up a refrigerator, including compressors, fan motors, and more, and explore their functions in detail.
- Compressor:
The heart of a refrigerator, the compressor is responsible for circulating the refrigerant throughout the unit. Its primary function is to compress the low-pressure gas refrigerant, raising its temperature and pressure. This compressed refrigerant then flows to the condenser. - Condenser:
Located at the back or bottom of the refrigerator, the condenser facilitates the transfer of heat from the refrigerant to the surrounding environment. As the compressed refrigerant passes through the condenser coils, it releases heat and condenses into a high-pressure liquid. The condenser fan motor helps to enhance the heat dissipation process, ensuring efficient cooling. - Evaporator:
The evaporator is located inside the refrigerator compartment and is responsible for cooling the air. It consists of a network of coils through which the liquid refrigerant passes, absorbing heat from the refrigerator’s interior. As the refrigerant evaporates, it transforms into a low-pressure gas and returns to the compressor to begin the cycle again. - Fan Motor:
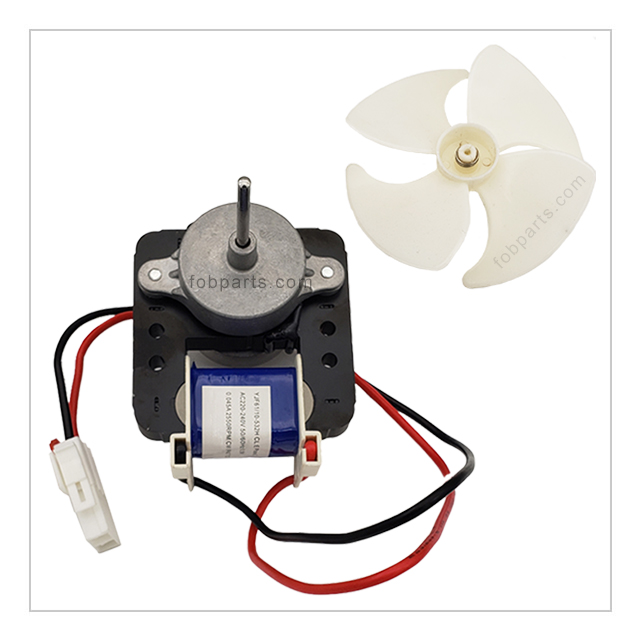
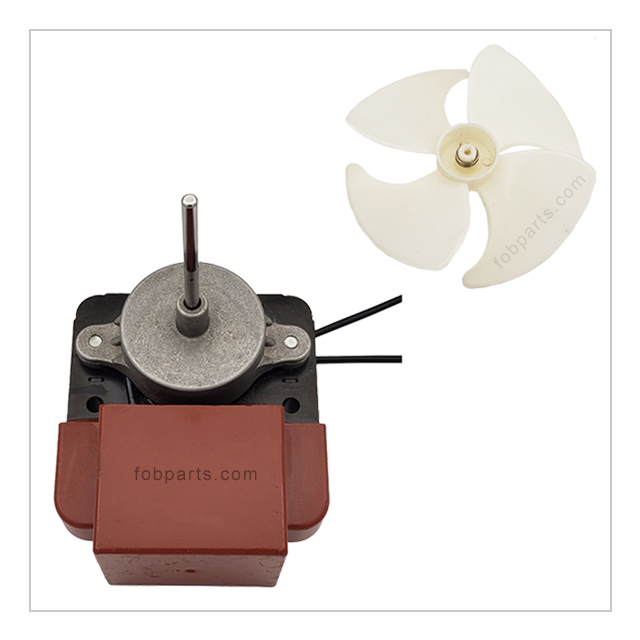
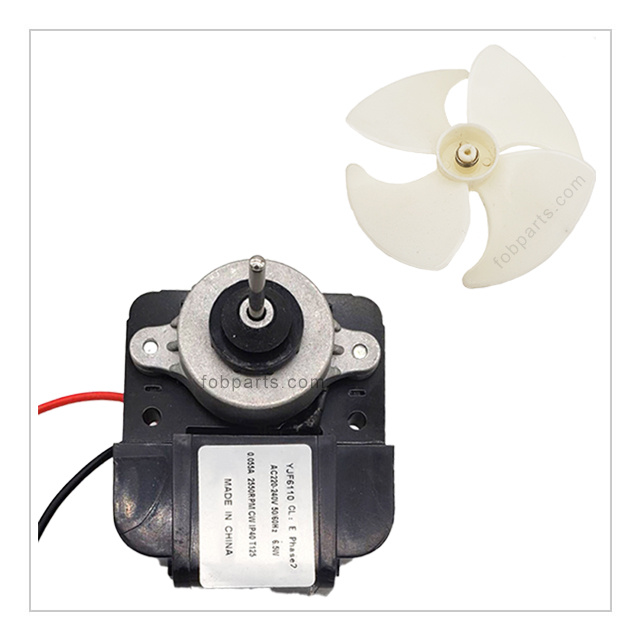
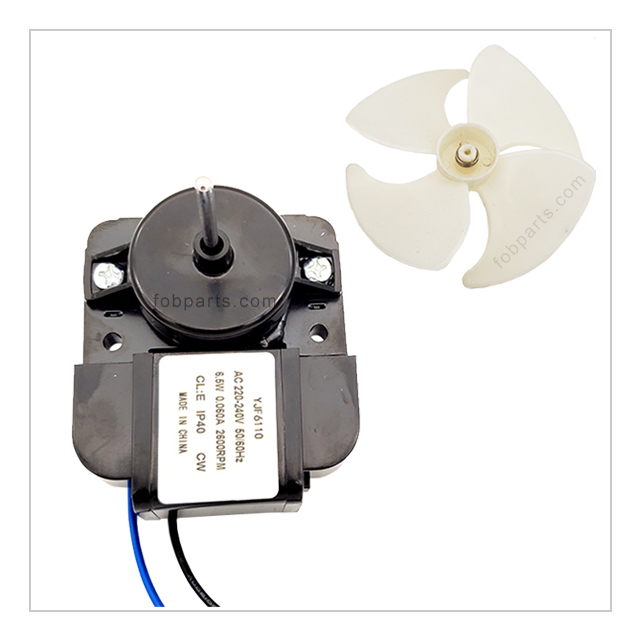
The fan motor plays a vital role in maintaining proper air circulation within the refrigerator. It helps to distribute cool air evenly throughout the compartments, ensuring that food items are kept at a consistent temperature. In addition, the fan motor aids in preventing frost buildup by circulating air over the evaporator coils, allowing for efficient defrosting. - Thermostat:
The thermostat acts as the control center of the refrigerator, regulating the temperature based on user settings. It senses the temperature inside the unit and signals the compressor to turn on or off accordingly. By maintaining a constant temperature, the thermostat helps to prolong the freshness and quality of stored food. - Defrost Heater:
To prevent excessive frost buildup on the evaporator coils, refrigerators are equipped with a defrost heater. This heating element is responsible for melting accumulated ice and frost during the defrosting cycle. It ensures that the evaporator coils remain free from ice, enabling efficient cooling and preventing potential damage to the unit.
Conclusion:
The internal components of a refrigerator work in harmony to create a reliable and efficient cooling system. From the compressor to the fan motor, each part has its unique function, contributing to the overall performance of the appliance. Understanding these components and their roles can help users troubleshoot issues and appreciate the complexity behind the seemingly simple task of keeping our food fresh and cool. So, the next time you open your refrigerator, take a moment to appreciate the intricate mechanisms that make it all possible.